Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy is widely known as a progressive muscle wasting disease, but there’s more to Duchenne than that. While the lack of dystrophin definitely affects muscles, it also affects behaviors and relationships, too. Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy is far, far more than just a muscle disease and the information below illustrates just that.
And for populations that may benefit from different explanations of Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy, please visit these links: children, educators, physical therapists, medical community.
Learn more here:

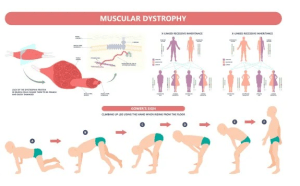
DMD is largely known for its debilitating effects on the musculoskeletal system, eventually affecting the individual’s ability to walk. However, muscles are an integral part of all our bodies, and many other bodily systems are affected in DMD besides the musculoskeletal:
- Bone Density
- Cardiac (heart)
- Gastroenterology (digestion & elimination)
- Emergency Contraindications
- Endocrinology (hormones)
- Pulmonary (breathing)
Since there is also a lack of dystrophin in the brain, the effects of Duchenne don’t stop with the muscles. DMD also affects the brain, emotions, and behaviors – often with little mercy.
- 4 Factors in Meltdowns
- Challenging Behaviors
- Learning Differences
- Medication Side Effects
- Mental Health Comorbidities
- Not Just a Muscle Disease
- Situations that Fuel Meltdowns
- The Duchenne Spectrum of Behaviors
Relationships & Social Effects
It may come as no surprise, then, that individuals with Duchenne often behave in ways that are socially unexpected. They might fixate on ideas, avoid eye contact, interrupt repeatedly, not talk at all, show hyperactivity, and meltdown when changing activities. The relationships of the individual and his family simply can’t be unaffected.
In fact, families often report that these emotional and social challenges are the hardest part of Duchenne to bear.

- Adolescence Interrupted
- Adult Friendship Challenges
- Barriers to Inclusion
- Building Meaningful Relationships
- Identity Formation
- Interdependence
- Social Isolation
- The Need for Human Touch
- When You Stop Walking
These factors only begin to illuminate life with Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy. The disease is vastly complicated, and we invite you to browse our website to learn more.




